What Is It?
Overclocking simply means getting components of your computer to perform above levels which are considered optimum.
Since one particular part of the computer cannot operate independently, when overclocking is set into motion, the software doing this has to initiate changes in other areas as well to make sure the device doesn’t break down due to overload.
How Does It Work?

The fan can go only so far as its cooling ability is concerned.
Your computer’s CPU is like its engine that is a well-known fact. But one thing many people are not aware of is that your processors are capable of running at higher speeds than what is stated as their optimum level. The reason is that the officially stated speed of your processor is the one best suited for it.
But it does not mean that if your processor is run at a higher speed, it will immediately break down. This is where overclocking comes in. Certain applications push your processor to go beyond its normal speed.
This, obviously, requires your processor to get more energy and thus it increases the voltage at which it is operating. Consequently, this would result in greater heating of your CPU and as a result you need the in-built fan of your CPU to also function at more than its normal level.
Here it is important to mention that the fan can go only so far as its cooling ability is concerned. Therefore, some people who are keen to overclock their systems either replace their coolers with more powerful ones or get an extra one installed to increase the cooling.
Coming back to the processor, it is pretty clear that it cannot function at a higher speed, which is measured in mega- or gigahertz) in isolation. Other components of the system also need to raise their level. This includes memory as well. Luckily, computer’s memory too is very much capable of performing at levels higher than stated by the manufacturer.
So, overclocking is a method through which your computer’s processor starts working at a higher speed than what the producer says it is capable of.
By drawing more voltage than normal, your processor raises its bar to a higher level, in the process, generating more heat. It also makes your system’s RAM work at a higher pace than its officially stated capacity.
The heat that is generated by all this hyper-activity then needs to be dispersed in a safe manner so that the system doesn’t suffer. This is achieved by making your system’s cooling fan work harder.
That is overclocking in a nutshell. More detailed information can be had here.
Why Is It Needed?

The heat that is generated by all this hyper-activity then needs to be dispersed in a safe manner so that the system doesn’t suffer.
A computer’s CPU is very capable of running basic programs with basic video and graphic qualities. But for software like games which contain heavy graphics and therefore increase the workload of the computer, a normal processor may not be sufficient. Hence, most users these days purchase PC’s loaded with graphic cards or GPU’s to take care of these more complex software’s.
The reason people go for overclocking is to make sure that they can run these heavy programs even with processors that may not be ideal for them.
For example, a game with sharp graphics may require a more advanced graphics card than what you possess. Rather than buying an all-new graphics card and installing it, something that would be very cumbersome and expensive, most people will try and use the latent capacity of their processors to make the game function. This is the main reason people opt for this option.
Is It Safe?
 In modern times, overclocking is usually safe as the chips of processors are of good enough quality to handle more than their designated workload. But anything is dangerous and harmful if done in excess and this is where all computer users have to be careful. Excessive overclocking may push your CPU and memory to beyond their limit and therefore cause damage to your computer.
In modern times, overclocking is usually safe as the chips of processors are of good enough quality to handle more than their designated workload. But anything is dangerous and harmful if done in excess and this is where all computer users have to be careful. Excessive overclocking may push your CPU and memory to beyond their limit and therefore cause damage to your computer.
Another thing to remember is that while the quality of chips is generally very good these days, the manufacturing process is not absolutely foolproof. As a result, while some chips may be able to withstand greater workload without difficulty, some may be less capable. There is no way for a user to know about this quality of his processor’s chips. So, suddenly trying to boost your computer’s speed to a much higher level may be dangerous.
Also, remember that cooling of the system when excess heat is being generated due to overclocking is necessary. If your system’s cooler is unable to handle the heat, then also your computer is in serious danger.
This is another reason for overclocking in moderation and not looking for wondrous results in a hurry.
If, however, you go ahead with overclocking recklessly, the kind of issues you could face are crashing of the hard drive, damage to the chips of the processors and could irreparably damage your motherboard and memory. So, be very careful while attempting this.
Also, remember that different processors react differently to overclocking. While AMD or ATI cards can be overclocked relatively easily, Nvidia cards are more vulnerable to damage during this process.
Also, overclocking voids manufacturer’s warranty in many cases. So, any damage you do will have to be repaired at your own expenses.
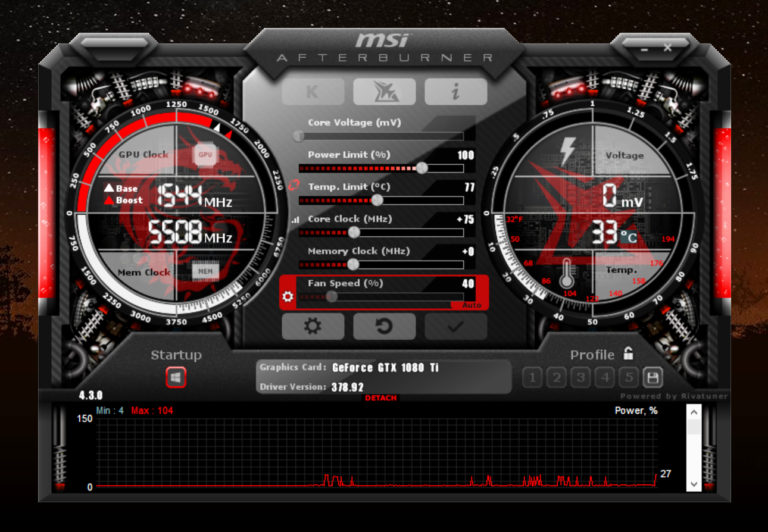
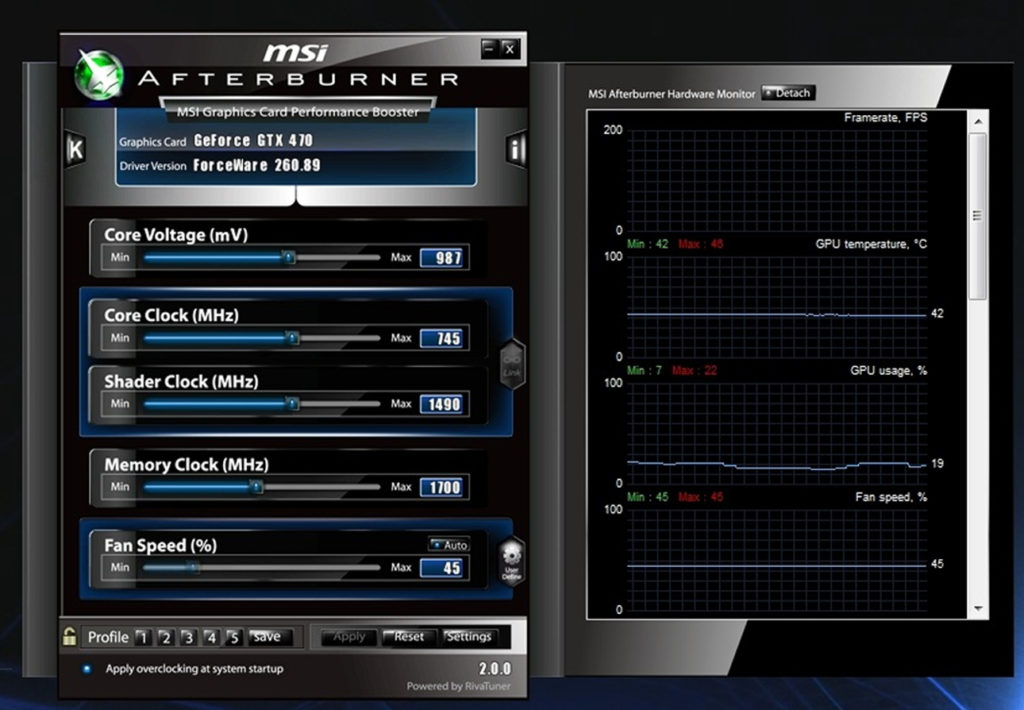
Is It Necessary To Overclock Through Downloaded Software?
Many processors now come with an in-built overclocking mechanism that can be activated. This means that you can achieve the same type of results without using an external software. The overclocking settings can be accessed in most systems through BIOS. There you can choose which type of overclocking setting (automatic, semi-automatic or manual) you want for your system.
Earlier, most processors used to be clock-locked which meant that they couldn’t be overclocked to above the limit set for them. This is no longer the case in most cases and therefore overclocking, automatic or manual, is now possible for most system.
Is It Worth It?
Unless you are engaged in work that requires heavy work related to graphics like 3D gaming, there is no great need for overclocking as basic activities will continue to operate in the same way.






0 Comments